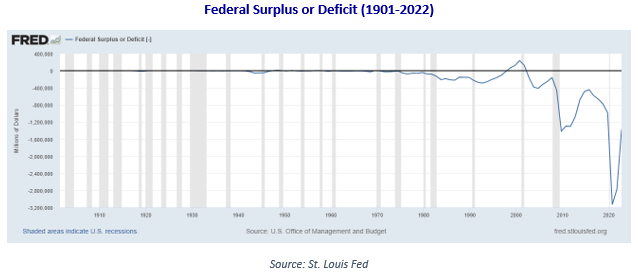
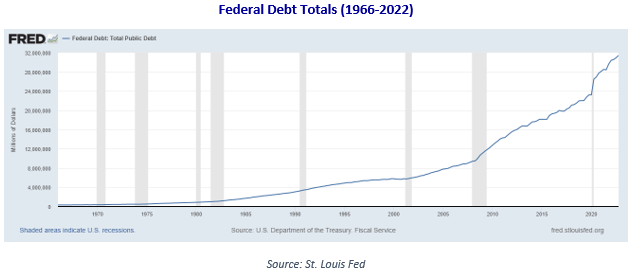
Rethinking Risk in an Uncertain World
Risk is an incredibly broad term, particularly in the investment world. Risk encompasses a range of factors, situations, and possibilities impacting one’s portfolio. Risk is also inherently relative. The field of behavioral finance tells us that everybody’s concept of risk is different. Individual experiences inform each person’s perception and tolerance toward risk.
Markets invoke anxiety. This encourages some to escape rather than assess. Others are drawn toward uncertainty and assume undue risk. While our fight or flight response served us throughout evolution, it often leads to poor investment outcomes. Studies show that emotion-driven investors typically underperform.[1]
Risk biases drive harmful decisions. Our brains are hardwired to draw conclusions quickly. These mental shortcuts may rely upon incomplete information. Consider the nervous investor who sells their shares at market bottom. This trade might provide momentary emotional relief. However, that individual effectively locked in losses and forfeited any opportunity for recovery. The converse is also true. An investor may cling to a single high-performing stock. They remain steadfast until an unforeseen event wipes out their portfolio. Then there is the cash-flush individual who shuns markets entirely. While that individual avoids on-paper losses, inflation slowly erodes the portfolio’s spending power over time. Each situation represents an incomplete understanding of risk.
Fortunately, a structured investment plan will combat these inclinations. Risk analysis is a key step. This exercise considers one’s circumstances (risk capacity), beliefs (risk perception), and preferences (risk tolerance). The investor’s risk profile and goals then determine a suitable portfolio structure. This objective process allows individuals to separate emotional biases from actual threats.
Countless factors and influences impact portfolio performance. Some are manageable and others are not. Regardless, proper information can guide portfolio decisions and even reframe risk evaluations altogether. This article will outline several key risk categories affecting stocks and bonds.