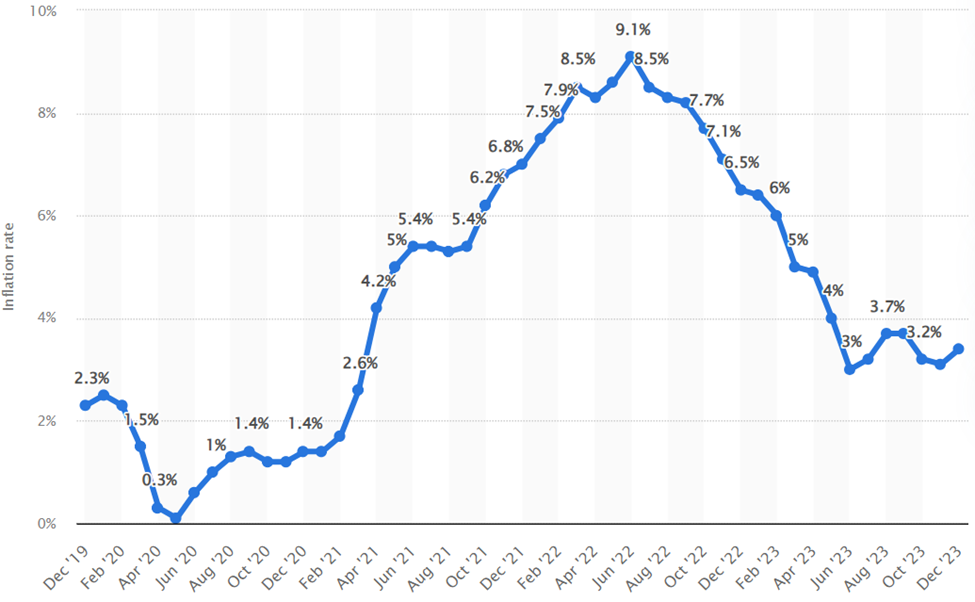
Central bankers used the term Transitory Inflation to explain a series of rapid price increases following the Covid-19 Pandemic. Inflation readings nearly doubled from 2.6% in March 2021 to 5% just two months later. Price increases eventually peaked at 9.1% in June 2022 before gradually decelerating.
The phrase implied that price increases were merely temporary and circumstantial.
Central bankers argued that supply chain disruptions, pent-up consumer demand from pandemic lockdowns, and available cash from stimulus actions were driving price increases. This theory posited that prices would quickly stabilize once producers and consumers readjusted.
Inflation ultimately proved stickier than the Federal Reserve anticipated. Economists point to government policy, job market disruptions, and corporate profit-taking as key culprits.
#inflation #transitory #Covid #FED



